Asprova Beginner's Lesson 10 -- Scheduling parameter --
30 minutes
Learn by Movie
Download the project file of this lesson.
If you take a look to the documentation, please read the following.
What you will learn in this lesson
Asprova is very flexible in how a schedule is executed using user-specified conditions and process parameters. This is because tasks in schedules are executed in units of commands, and the order in which commands are executed can be configured freely. In addition, scheduling parameters can be used to specify how commands are to be executed.
Scheduling parameters can be used to set the following kinds of conditions.
- Setting the assignment direction
Example: Assign operations so that production takes place at the earliest possible time. Or, assign operations as close to the due date as possible. - Setting items that determine the assignment order
Example: Assign operations on the basis of due dates and priorities in ascending order. - Setting items that are prioritized when operations are assigned to resources
Example: Prioritize production equipment with high capacity or prioritize load leveling when making assignments.

In this lesson, you will learn about scheduling parameters. In lesson 11, you will learn about the different types of commands and how to configure them.
The contents of this lesson apply to MS Light module + Scheduling parameter option and higher modules. The operations described here are for the MS Light module + Scheduling parameter option. For information on how to switch the module and option, see "How to start Asprova" and "How to switch option for Trial".
Download the project file of this lesson.
If you have questions, please access "Q&A Center" from navigation menu of this web site.
1. Assignment Direction: Forward and Backward
If you want operations to be assigned with minimal idle time, you can use forward scheduling. In forward scheduling, operations are assigned to begin at the earliest times possible beginning with the first process operation. Then by searching forward for idle times and taking into account time constraints the rest of the operations are scheduled.
On the other hand, if you want operations to be assigned so that productions are completed as close to the due dates as possible, you can use backward scheduling. In backward scheduling, operations are assigned in reverse order beginning with the last process operation. Then searching backward through the operations for idle time and following the constraints of the operations back to the first operation.
We use the [Assignment direction] scheduling parameter to specify forward scheduling or backward scheduling. First, let's take a few orders and see how the two assignment directions are applied to scheduling results.
■ Procedure
(1) Display the Scheduling parameter Settings dialog box, and check the [Forward scheduling] parameter.
Choose [Schedule]-[Scheduling Parameter Settings].

- Choose [Schedule]-[Scheduling Parameter Settings] to display the Scheduling parameter Settings dialog box.
(2) We can see that [Assignment direction] is set to [Forward].
the OK button to close the dialog box.

- [Assignment direction] is set to [Forward].
(3) Reschedule and check the scheduling result.
Operations have been assigned in order to the earliest times possible with minimal idle times beginning with the first process operation. This is the assignment result for forward scheduling.

(4) Now, let's try backward scheduling.
Check the [Assignment direction] of the [Backward scheduling] parameter. Choose [Backward Scheduling] from the scheduling parameter combo box.

- Choose [Backward Scheduling] from the scheduling parameter combo box to try backward scheduling.
(5) Choose [Schedule]-[Scheduling Parameter Settings]. We can see that [Assignment direction] is set to [Backward]. Click the OK button to close the dialog box.
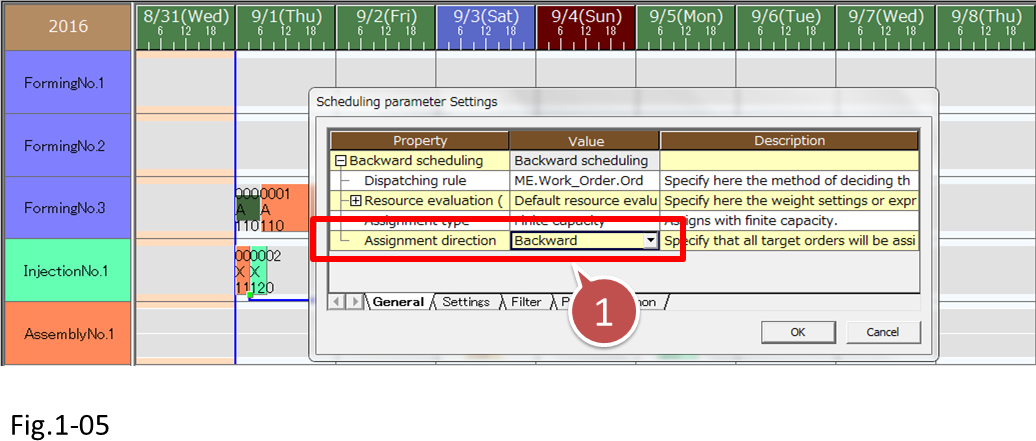
- [Assignment direction] is set to [Backward].
(6) Reschedule and check the scheduling result.
Operations have been assigned in order from the last process on the basis of the due date of each order with minimal idle times. This is the assignment result for backward scheduling.
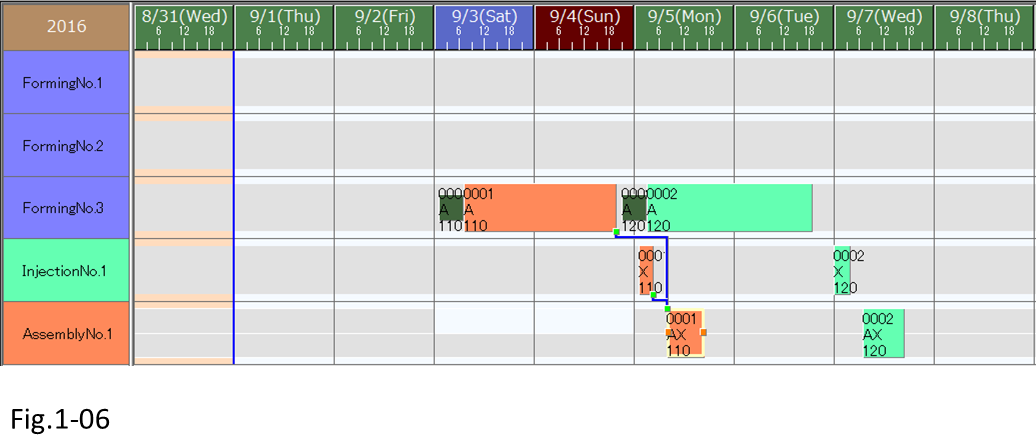
(7) Before proceeding to the next step, change the scheduling parameter combo box to [Forward scheduling].
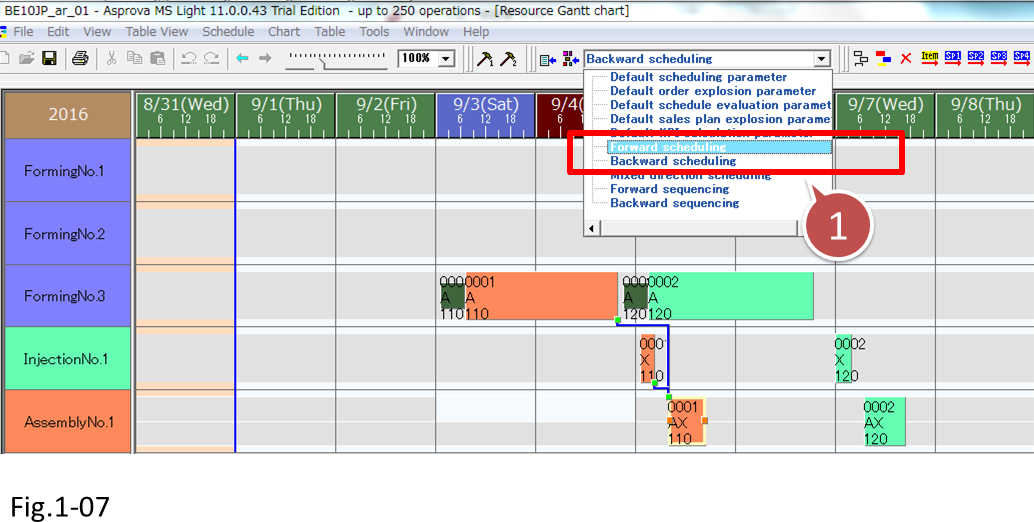
- Change the scheduling parameter combo box to [Forward scheduling].
Finite capacity scheduling and infinite capacity scheduling
Lesson 4 and earlier lessons used infinite capacity scheduling, lesson 5 and later lessons used finite capacity scheduling.
You can use the [Assignment type] scheduling parameter to select either infinite capacity scheduling or finite capacity scheduling.
• Scheduling parameter Settings dialog box
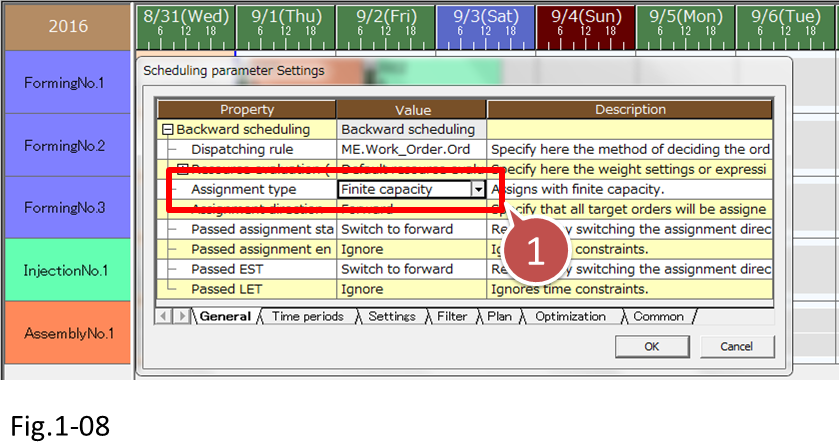
- [Assignment type] scheduling parameter to select either infinite capacity scheduling or finite capacity scheduling.
•When assignment type is set to [Finite Capacity]

•When assignment type is set to [Infinite Capacity].
2. Operation Assignment Order: Dispatching Rule
As we learned earlier, because operations are assigned by searching for idle times of resources, the earlier the assignment of an operation, closer the result of the assignment to the expected result. Therefore, the assignment order is an important setting parameter. The order in which operations are assigned is called the dispatching order and is specified using dispatching rules. In forward scheduling assignment, orders with earlier due dates and orders with higher priorities are generally assigned first.
■ Procedure
(1) Let's check the [Dispatching rule] of the [Forward scheduling] parameter.
Choose [Schedule]-[Scheduling Parameter Settings].
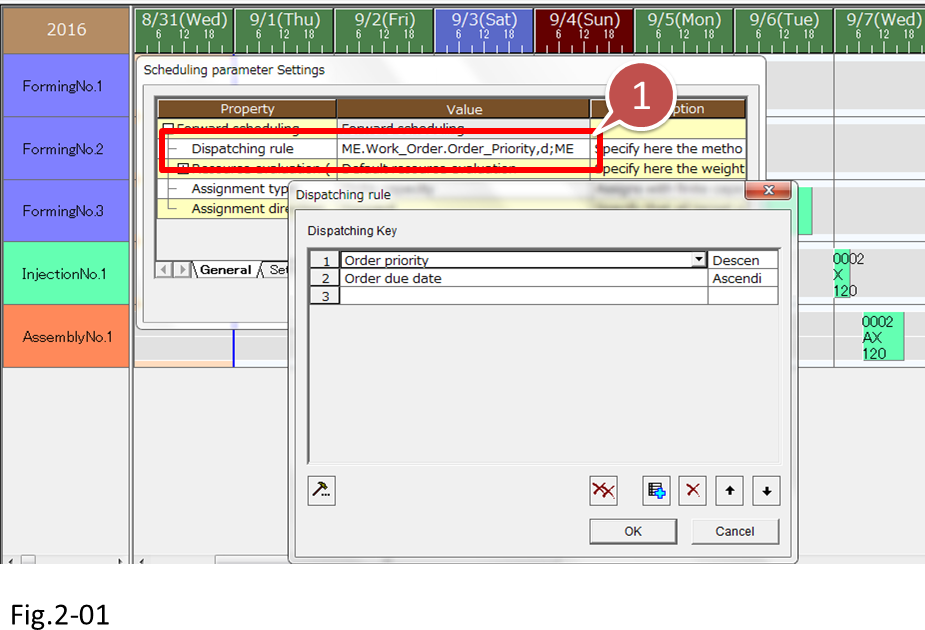
- Click the button that appears at the right edge of the cell when you select the cell. The Dispatching rule dialog box appears.
In the dispatching rule, [Order priority] is set to [Descending] and [Order due date] is set to [Ascending]. With these settings, the order with the highest priority is assigned first. For orders with the same priority, the order with the earliest due date is assigned first.
After checking the Dispatching rule settings, close all dialog boxes.
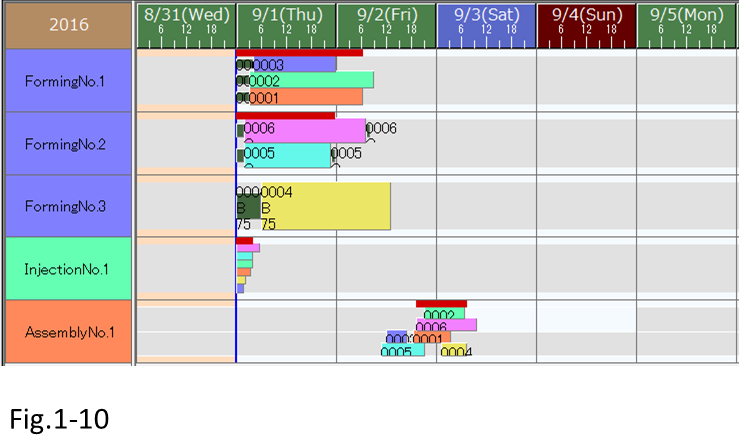
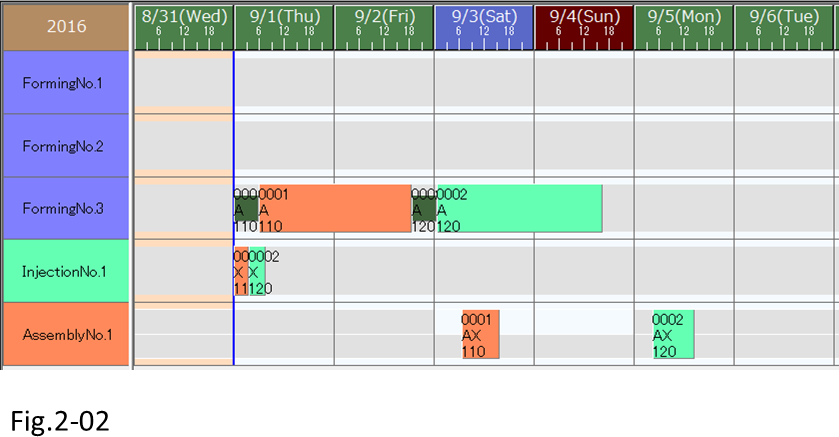
(2) Reschedule and check the scheduling result.
We see that order 0001 is going to be handled first.
(3) Let's check the information of each order in the Order table.
The priorities for both 0001 and 0002 are set to the default value , which is 80. Therefore, we see that 0001, whose due date is earlier, is dispatched first.
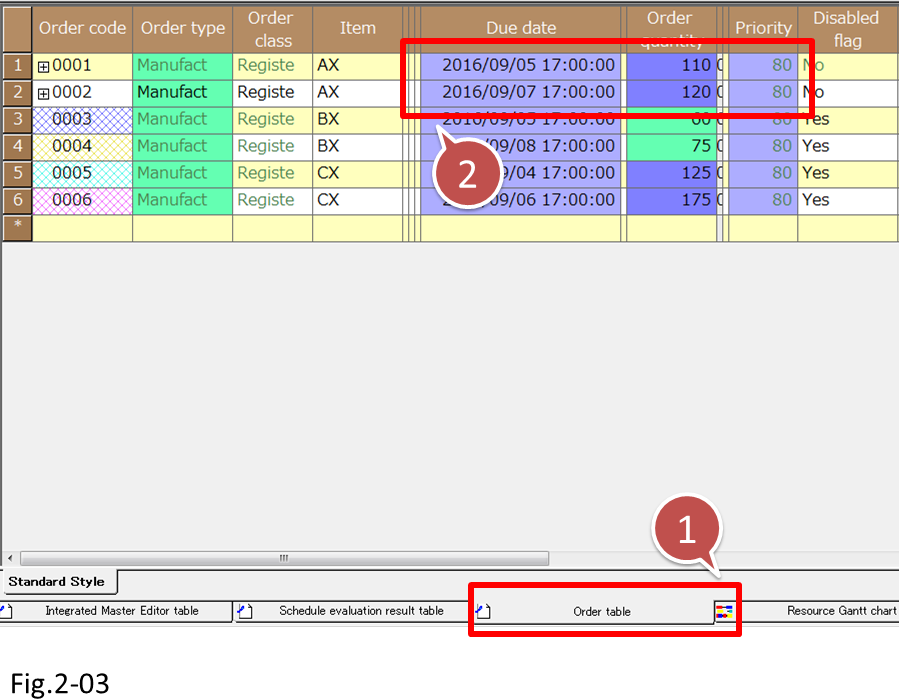
- Display the Order table.
- Order [0001], whose due date is earlier, is dispatched first.
(4) Let's change the priorities and verify that the order changes.
Change the priority of order 0002 to 99.
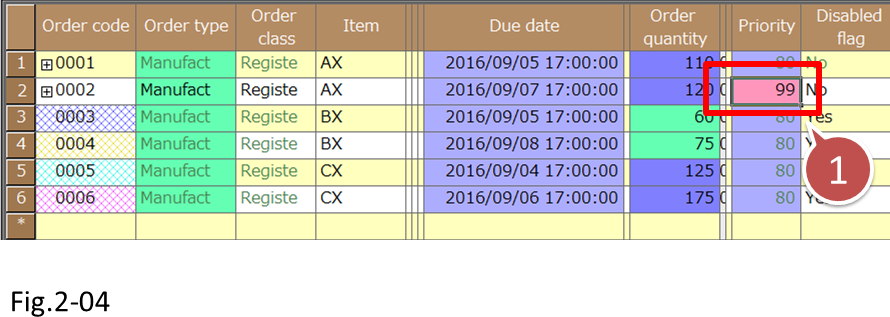
- Change the priority of order 0002 to 99.
(5) Execute a reschedule, and check the assignment result. We can see that order 0002, whose priority is higher, has been dispatched first.
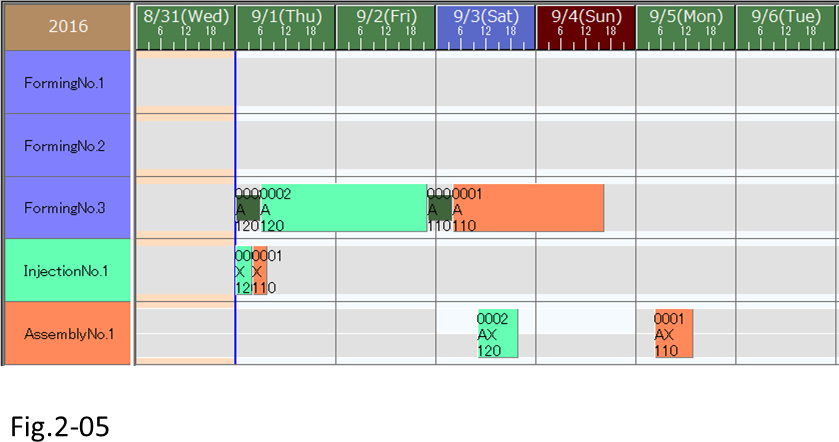
(6) Next, let's change the dispatching rule so that due dates are prioritized in dispatching. When we make this change, the order with the earliest due date is first.
Choose [Schedule]-[Scheduling Parameter Settings], and display the Dispatching rule dialog box.
Change the dispatching rule so that [Order due date], which is set to [Ascending], comes before [Order priority], which is set to [Descending].
After making this change, click the OK button to close the dialog box.

- Select the item that you want to move.
- Click the up or down button to change the order of the selected item.
(7) Reschedule and verify that order 0001 with the earlier due date is dispatched first in the scheduling result.
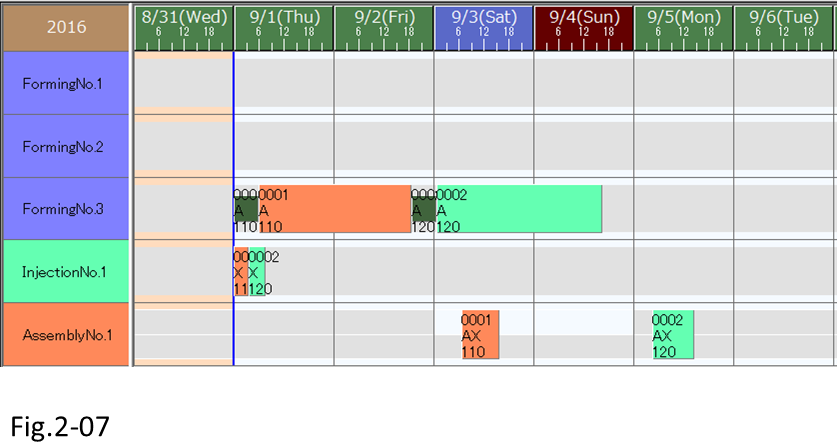
Items that you can specify for the dispatching rule
Dispatching order scheduling parameters can be added, changed, and deleted in the Dispatching rule dialog box.
In addition to the [Order due date] and [Order priority] items mentioned earlier, the items to use as dispatching order keys can be selected from a list.
For example, if you select Num spec 1, you will be able to dispatch items and orders depending on Num spec 1.
You can schedule so that orders with the same due date are dispatched in descending order by Num spec 1.

3. Assignment Control to Multiple Resources: Resource Evaluation
When there are multiple resources that an order can be assigned to, it is important to determine which resource the order is to be assigned to in order to obtain the optimal result. For example, using resources with the shortest production time is best, but if too many orders are assigned to resources with high manufacturing capacity, wait time of following processes could be longer. In such a case, we may want to level the load. These sort of conditions can be specified in [Resource evaluation] in order to control the assignment to resources.
■ Procedure
(1) Let's change the [Disabled flag] in the Order table so that all orders will be assigned.
Change the [Disabled flag] of orders BX and CX to [No].
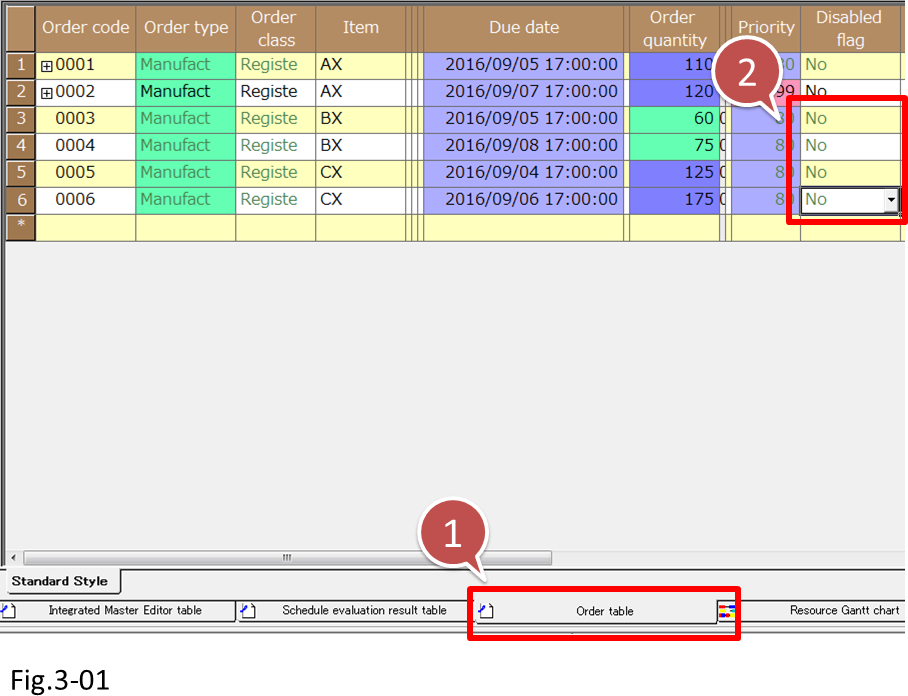
- Display the Order table.
- Change the [Disabled flag] of orders BX and CX to [No].
(2) Reschedule and check the scheduling result.
There are three Forming process resources, but resource Forming No. 1 has no operations assigned to it.

(3) Let's check the Integrated Master table.
We can see that the Use instructions of the Forming processes of item AX and BX are set so that assignment to Forming No.1 is possible and that the manufacturing capacity is higher than that of Forming No.3.
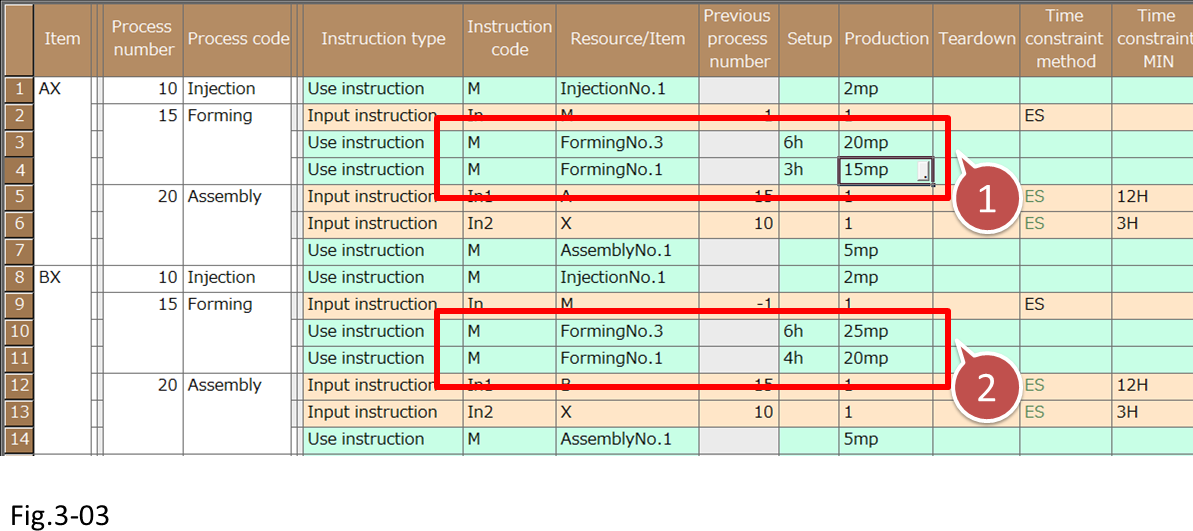
- Assignment to Forming No.1 is possible and that the manufacturing capacity is higher than that of Forming No.3.
(4) Let's now set the [Resource evaluation] scheduling parameter.
Display the [Forward scheduling] parameter Settings dialog box, and check the Resource evaluation setting. Expand and click the arrow icon next to [Default resource evaluation]. The details of the Resource evaluation that you clicked are displayed in a new dialog box.
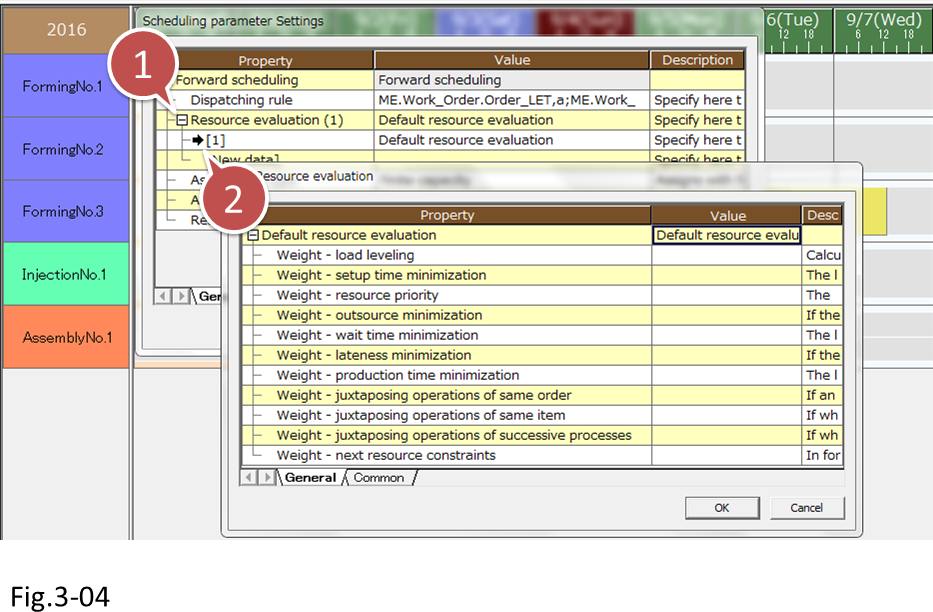
- Click the + icon to expand
- Click the arrow icon to display the Edit Resource evaluation dialog box.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Load leveling | Priority is given to selecting the resource with the least load. |
| Setup time minimization | Priority is given to selecting the resource with the minimal setup time when the operation is assigned. |
| Resource priority | Priority is given to selecting the resource with the highest Resource priority in the Master use instruction of the Integrated Master. |
| Outsource minimization | Priority is given to selecting resources whose Resource type is not set to "Outsource resource." |
| Wait time minimization | Priority is given to selecting the resource that results in the minimum wait time to the previous process in the case of forward scheduling and to the following process in the case of backward scheduling. |
| Lateness minimization | Priority is given to selecting resources that would not cause due date delays when operations are assigned. |
| Production time minimization | Priority is given to selecting the resource with the minimum production time when the operation is assigned. |
| Juxtaposing operations of same order | Priority is given to selecting resources that have the operations of the same order assigned. |
| Juxtaposing operations of same item | Priority is given to selecting resources that produce the same item in juxtaposing operations. |
| Juxtaposing operations of successive processes | Priority is given to selecting resources that would cause the left-adjacent (or right-adjacent) operation to be the operation of previous (or following) process when the operation is assigned. |
| Next resource constraints | For forward scheduling, priority is given to selecting resources that are contained in the [next resource constraints] of the resource that the previous process operation is assigned to. For Backward scheduling, priority is given to selecting resources that are contained in the [next resource constraints] of the resource that the following process operation is assigned to. |
There are 11 items that are used to determine which resource is selected when operations are assigned to resources. We assign weighting to these items to specify how much an item is prioritized over other items. Larger the difference in relative weighting, higher the tendency for the weighting to affect the resource selection.
For details on weighting, see the following table. (For details, see "Evaluation" in the online help.)
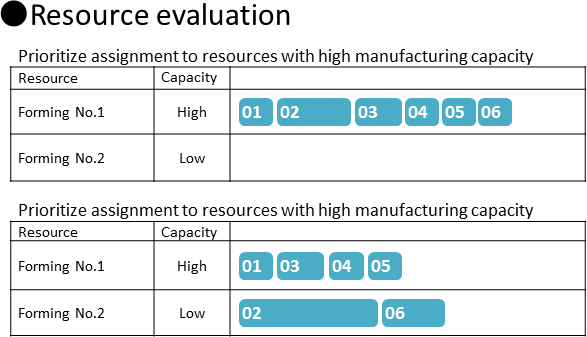
Here, we will set [Weight - production time minimization] to 1 so that priority is given to selecting resources with high manufacturing capacities.
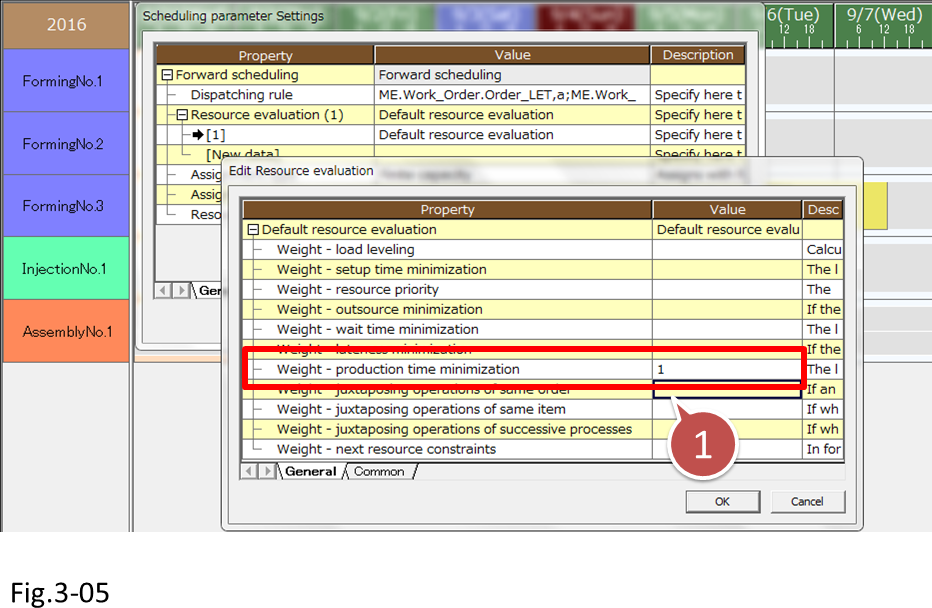
(5) Reschedule and check the scheduling result.
Operations have been assigned to Forming No.1, which has a high manufacturing capacity. On the other hand, no operations have been assigned to Forming No.3, which has a low manufacturing capacity.

This is because only [Weight - production time minimization] has been specified, and other weighting parameters have not been applied to the resource selection.
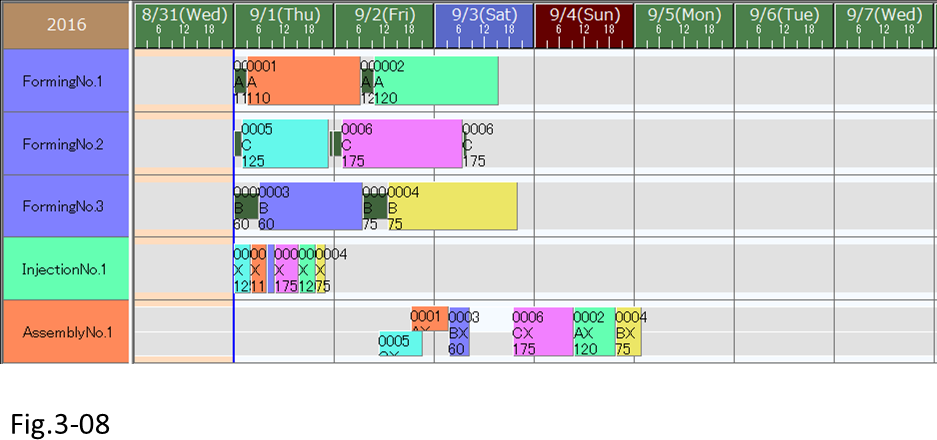
(6) Let's assign operations also to Forming No.3, which has a low manufacturing capacity, in order to level the load.
We will change the Resource evaluation of the [Forward scheduling] parameter. Display the Edit Resource evaluation dialog box, and set [Weighting - load leveling] also to 1.

(7) Reschedule and check to see whether the load is leveled. Operations have also been assigned to Forming No.3, and the load on the Forming operation resources has been leveled.
Scheduling parameters available in MS Light
In MS Light, you can use the following two scheduling parameters even if you do not have the Scheduling parameter option or the Scheduling command option.
* To edit scheduling parameters, you need the Scheduling parameter option. To create new scheduling parameters, you need the Scheduling command option (see lesson 11).
• Forwards schedule
Operations are assigned in order so that they are started as soon as possible starting with the first process.
• Backwards schedule
Operations are assigned in order starting with the last process. Operations are assigned as close to the due date as possible.
The dispatching rules available for each of these parameters are shown below.
| Forwards schedule | Backwards schedule | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Order Due date (ascending) | Order Due date (descending) |
| 2 | Spec 1 (ascending) | Spec 1 (ascending) |
| 3 | Spec 2 (ascending) | Spec 2 (ascending) |
| 4 | Spec 3 (ascending) | Spec 3 (ascending) |
| 5 | Spec 4 (ascending) | Spec 4 (ascending) |
The weighting of the following resource evaluation parameters for these scheduling parameters are set to 1.
Related Materials
For more details on scheduling parameters, see the following materials.